Redis
中文官网http://www.redis.cn/commands.html#sorted_set
一 五种基础类型和三种特殊类型
keys * 查看当前库所有的key
exists name 判断name键是否存在
expire name 10 设置name键的过期时间为10秒
ttl name 查看name的剩余过期时间
type name 查看name键的类型
flushall 清空所有数据库
flushdb 清空当前数据库
1. String类型
set key value ---> set name zhang 设置key为name,值为zhang
append key value ----> append name san 向name后添加字符串,如果name不存在,就等价于set name san
strlen key ---->strlen name 获取name 的长度
incr key --->incr view 在view的基础上加1(自增1)
decr key --->decr view 在view的基础上减1(自减1)
incrby key number -->incrby view 10 在view 的基础上加10
decrby key number --->decrbu view 10 在view 的基础上减10
getrange key start end ---->getrange name 0 3 截取name值得0到3位,类似java的substring(如果是getrange name 0 -1 则和get name一样)
setrange key index value ---> setrange name 1 ‘66’ 将name的值的第2位值替换为66
setex key secend value ------> setex name 20 ‘666’ 新建一个key name,将过期时间设置为20秒后
setnx key vaule --->setnx name zhangsan 创建一个key name,如果name存在,则不创建。如果不存在,则创建
mset key1 value1 key2 value2 ... -------批量创建key value
mget key1 key2 key3..... -------批量获取key
msetnx key1 value1 key2 value2 ... -------批量创建key value,不存在的key再创建(该操作是原子性操作,要成功一起成功,要失败一起失败)
getset key value ----------先获取值,再设置新的值
2. List类型
list可以作为栈,队列,阻塞队列
lpush key value ----------向集合里面存放值,从头部插入
lrange key start end -------------获取集合内的值,从下标start开始 end结束(start=0 end=-1为查询所有)
rpush key value ----------向集合里面存放值,从尾部插入
lpop key ----------移除集合key内的头部(左边)第一个值
rpop key ----------移除集合key内的尾部(右边)第一个值
lindex key index --------------通过下标index获取集合key中的值
llen key -------------获取集合key的长度
lrem key count value -----------移除集合key中指定数目count的value值
lrange key start end -------------通过下标(下标值从1开始)截取指定长度的集合,从头部开始
rpoplpush key1 key2 -------------将key1集合的最后一个元素移出,然后存放进key2中
lset key index value ------------将集合key中的下标index元素值设置为value,相当于更新操作(key必须存在,可以使用exists list 判断当前集合是否存在,index也必须存在)
linsert key before/after pivot element -------- 将值element插入到列表key中的元素pivot 的前面或后面。示例如下
127.0.0.1:6379>lrange list 0 -1
1)"1"
2)"2"
3)"3"
127.0.0.1:6379> linsert list before 2 1.1
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange list 0 -1
1)"1"
2)"1.1"
3)"2"
4)"3"
127.0.0.1:6379>
小结:
1. 实际上是一个链表, before node after,left ,right 都可以插入值
2. 如果key不存在,创建新的链表
3. 如果key存在,新增内容
4. 如果移除了所有值,空链表,也代表不存在
5. 在两边插入或者改动值,效率最高,中间的元素相对效率较低
3.Set
set中的值是不可重复的!
sadd key value1 value2 value3..... ---------向集合key内添加值
smemerbers key -----------查看集合内的所有值
sismember key value ------------判断值value是否在key中
scard key ------------获取set集合中的元素个数
srem key value -------移除set集合中的指定元素
srandmember key count --------随机抽取出count个元素
spop key ----------------随机删除集合中的元素
smove key1 key2 element ---------------将元素element从key1中移到key2中
sdiff key1 key2 ------------获取集合中的差集
sinter key1 key2 ------------获取集合中的交集(可以判断共同好友,共同关注,共同爱好等等)
sunion key1 key2 ------------获取集合中的并集
4.hash(哈希)
map集合,key-value。和string类型类似,只不过此处将vaule值换成了map
应用:经常变更的数据,尤其是用户类的信息。hash更适合对象存储,string适合字符串存储
hset key field value -----------将key值中存放map值 (field和value)
hget key filed --------------获取key值中的map的key为 filed的值
hmset key [field value].... -------------批量设置map的值
hmget key filed1 filed2.... ------------批量获取key的value值
hgetall key -------------获取key值的所有键值对数据
hdel key filed。。。 ------------------删除key中指定的filed值
hlen key ---------------获取key中的字段数量
hexists key filed ----------------判断指定字段filed是否存在
hkeys key ------------获取所有的字段filed值
hvals key -----------获取所有的value值
hincrby key filed value -------------将key中的filed值指定value增量
hsetnx key filed value --------------如果key中的filed不存在则设置值,如果存在则不操作
5. zset (有序集合)
zadd key socre value -----------向集合中添加元素value 排序值为score,可以一次添加多个
ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max -----------返回min和max排序之间的成员,排序由低到高(-inf负无穷小 +inf 正无穷大)
zrem key value1 value2 value3.... -----------------移除集合中的指定元素
ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min -------------返回min和max排序之间的成员,排序由高到低
zrange key indexstart indexend --------取集合中下标从start到end的值,由低到高排序
zrevrange key indexstart indexend --------取集合中下标从start到end的值,由高到低排序
zrange key indexstart indexend withscores ----取集合中下标从start到end的值,由低到高排序,并返回对应的score值
zcount key start end ----------- 统计集合中值在start到end的个数
zadd rank incr 1 zhangsan -------将集合 rank中zhangsan的socre增长1.如果不存在,则添加
应用:
工资表排序,班级成绩
消息带权重排序。
排行榜
6. 地理空间(geospatial)
tips:底层基于zset实现
geoadd key 经度 维度 名称 。。。。。。。 ----------添加元素对应的经度维度
GEODIST key element1 element1 unit -------------计算两个元素之间的直线距离 unit单位m km mi(英里) ft(英尺)默认米
GEORADIUS key 经度 维度 半径 单位 [count number] ----------通过指定的经度维度查询出对应半径内的指定number个数对象。不传count number查所有
GEORADIUSBYMEMBER key element radius unit -----------这个命令和 GEORADIUS 命令一样, 都可以找出位于指定范围内的元素, 但是 GEORADIUSBYMEMBER 的中心点是由给定的位置元素决定的, 而不是像 GEORADIUS 那样, 使用输入的经度和纬度来决定中心点指定成员的位置被用作查询的中心。
7.hyperloglogs
用于基数(不重复的值)运算,允许少量容错。

pfadd key element1 element2 element3......... --------------向key中添加元素
pfcount key -----------------计算key中的基数
pfmerge newkey key1 key2 -------------------将key1和key2的元素合并为新的newkey
8.bitmaps

setbit key 检索位 1/0 -------------该SETBIT命令将位号作为其第一个参数,将其设置为1或0的值作为其第二个参数
bitcount key -----------------获取设置为1的个数
二 事务
1. 事务简介
MULTI 、 EXEC 、 DISCARD 和 WATCH 是 Redis 事务相关的命令。事务可以一次执行多个命令, 并且带有以下两个重要的保证:
事务是一个单独的隔离操作:事务中的所有命令都会序列化、按顺序地执行。事务在执行的过程中,不会被其他客户端发送来的命令请求所打断。
事务是一个原子操作:事务中的命令要么全部被执行,要么全部都不执行。EXEC 命令负责触发并执行事务中的所有命令。
如果客户端在使用 MULTI 开启了一个事务之后,却因为断线而没有成功执行 EXEC ,那么事务中的所有命令都不会被执行。
另一方面,如果客户端成功在开启事务之后执行 EXEC ,那么事务中的所有命令都会被执行。
当使用 AOF 方式做持久化的时候, Redis 会使用单个 write(2) 命令将事务写入到磁盘中。
然而,如果 Redis 服务器因为某些原因被管理员杀死,或者遇上某种硬件故障,那么可能只有部分事务命令会被成功写入到磁盘中。
如果 Redis 在重新启动时发现 AOF 文件出了这样的问题,那么它会退出,并汇报一个错误。
Redis事务没有没有隔离级别的概念!
- 所有的命令在事务中,并没有直接被执行!
- 只有发起执行命令的时候才会执行!
- ExecRedis单条命令式保存原子性的,但是事务不保证原子性!
5. 事务的两种情况
队列中的命令在入队的时候出错,则整个事务中的的命令都不会被执行,如
127.0.0.1:6379> multi oK 127.0.0.1:6379>set name zhangsan QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>set age 20 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> set height 175 a QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> seta errortemp (error)ERR unknown command 'seta', with args beginning with: 'errortemp', 127.0.0.1:6379> get age QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>exec (error) EXECABORT Transaction discarded because of previous errors. 127.0.0.1:6379>队列中的命令在运行的时候出错,则出错的命令报错,其他命令正常执行!如
127.0.0.1:6379> NULT1 oK 127.0.0.1:6379> set name zhangsan QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>incr name #自增只能用于integer类型,故意设置错误 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> set age 20 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> set height 175 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>get name QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> exec 1)oK 2)(error) ERR value is not an integer or out of range 3)oK 4)OK 5)"zhangsan" 127.0.0.1:6379>
2.redis实现乐观锁
1. 正常执行情况
先使用watch命令,监视对应的key
开启事务
命令队列执行
执行事务
效果如下
127.0.0.1:6379> watch money 0K 127.0.0.1:6379> multi OK 127.0.0.1:6379>decrby money 20 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>incrby user 20 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>exec 1)(integer) 980 2)(integer) 20 127.0.0.1:6379>
2.异常执行情况
先使用watch命令,监视对应的key
开启事务
将命令加入队列,如下
127.0.0.1:6379> watch money OK 127.0.0.1:6379>multi OK 127.0.0.1:6379>decrby money 100 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>incrby use 100 QUEUED此时另一个线程对被监视的key值做了修改,如下
127.0.0.1:6379>set money 1200 oK此时执行第三步的队列,效果如下
127.0.0.1:6379> watch money OK 127.0.0.1:6379> multi OK 127.0.0.1:6379>decrby money 100 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>incrby use 100 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379>exec (nil) 127.0.0.1:6379>分析:watch监视的money字段,在被另外一个线程修改后,版本号发生了改变,所以会导致修改失败。此时可以使用unwatch 命令取消监视,然后再次执行(监视,开启事务,命令加入队列,执行事务)。如果没有执行成功,循环该操作。类似于CAS自旋锁。
三 乐观锁
使用watch命令,对需要加锁的对象加锁,然后开启事务,在事务中操作该对象,如果在执行该事务之前,另外的线程修改了该值,则该事务会修改失败.
如果修改失败.使用unwatch命令,解除对需要修改的对象加锁,再加锁,然后配合java的无限循环实现
redis分布式锁(可见另一篇博客,redisson学习)
mysql分布式锁的实现--------- 进行一个修改版本version的判断,如果version在修改的时候和获取的时候一致,则可以进行修改
四 Jedis和luttuce
1 . jedis
采用直连的方式,多个线程操作的时候是不安全的,可以采用jedis pool解决。BIO阻塞IO
2. lettuce
底层使用netty,实例可以在多个线程中共享。 NIO 异步io
五 消息订阅
SUBSCRIBE chanel ---------订阅频道,然后会一直接收该频道的信息
PUBLISH chanel msg ----------向频道内发送消息
Redis是使用C实现的,通过分析Redis源码里的pubsub(文件,了解发布和订阅机制的底层实现,籍此加深对Redis 的理解。Redis通过PUBLISH、SUBSCRIBE 和PSUBSCRIBE等命令实现发布和订阅功能。
通过SUBSCRIBE 命令订阅某频道后,redis-server里维护了一个字典,字典的键就是一个个channel,而字典的值则是一个链表,链表中保存了所有订阅这个channel的客户端。SUBSCRIBE命令的关键,就是将客户端添加到给定channel的订阅链表中。通过PUBLSH命令向订阅者发送消息,redis-server会使用给定的频道作为键,在它所维护的channel字典中查找记录了订阅这个频道的所有客户端的链表,遍历这个链表,将消息发布给所有订阅者。
Pub/Sub从字面上理解就是发布(Publish)与订阅( Subscribe ),在Redis中,你可以设定对某一个key值进行消息发布及消息订阅,当一个key值上进行了消息发布后,所有订阅它的客户端都会收到相应的消息。这一功能最明显的用法就是用作实时消息系统,比如普通的即时聊天,群聊等功能。
六 redis配置文件
1. redis配文件置对大小写不敏感
# Redis configuration file example
# Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specify
# it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth:
#
# 1k => 1000 bytes
# 1kb => 1024 bytes
# 1m => 1000000 bytes
# 1mb => 1024*1024 bytes
# 1g => 1000000000 bytes
# 1gb => 1024*1024*1024 bytes
#
# units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same. #redis配文件置对大小写不敏感
2. 可以将多个配置文件配置到一个文件中
################################## INCLUDES ###################################
# Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you
# have a standard template that goes to all Redis servers but also need
# to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include
# other files, so use this wisely.
#
# Notice option "include" won't be rewritten by command "CONFIG REWRITE"
# from admin or Redis Sentinel. Since Redis always uses the last processed
# line as value of a configuration directive, you'd better put includes
# at the beginning of this file to avoid overwriting config change at runtime.
#
# If instead you are interested in using includes to override configuration
# options, it is better to use include as the last line.
#
# include .\path\to\local.conf #可以包含该路径下的配置文件
# include c:\path\to\other.conf#可以包含该路径下的配置文件
3.绑定ip
################################## NETWORK #####################################
# By default, if no "bind" configuration directive is specified, Redis listens
# for connections from all the network interfaces available on the server.
# It is possible to listen to just one or multiple selected interfaces using
# the "bind" configuration directive, followed by one or more IP addresses.
#
# Examples:
#
# bind 192.168.1.100 10.0.0.1
# bind 127.0.0.1 ::1
#
# ~~~ WARNING ~~~ If the computer running Redis is directly exposed to the
# internet, binding to all the interfaces is dangerous and will expose the
# instance to everybody on the internet. So by default we uncomment the
# following bind directive, that will force Redis to listen only into
# the IPv4 lookback interface address (this means Redis will be able to
# accept connections only from clients running into the same computer it
# is running).
#
# IF YOU ARE SURE YOU WANT YOUR INSTANCE TO LISTEN TO ALL THE INTERFACES
# JUST COMMENT THE FOLLOWING LINE.
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
bind 127.0.0.1 #绑定指定ip
4.配置端口
# Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379 (IANA #815344).
# If port 0 is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket.
port 6379
5.是否以守护线程开启,默认是no 需要修改为yes
################################# GENERAL #####################################
# By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it.
# Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemonized.
# NOT SUPPORTED ON WINDOWS daemonize no
daemonize yes
6. 如果是以守护线程开启的,必须设置对应端口的pid
pidfile /var/run/redis.pid #可以指定路径
windows不支持
# NOT SUPPORTED ON WINDOWS pidfile /var/run/redis.pid
7. 日志级别
# Specify the server verbosity level.
# This can be one of:
# debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing)
# verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level)
# notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably)
# warning (only very important / critical messages are logged)
loglevel notice
8. 日志文件名
# Specify the log file name. Also 'stdout' can be used to force
# Redis to log on the standard output.
logfile ""
9. 数据库数量,默认为16个
# Set the number of databases. The default database is DB 0, you can select
# a different one on a per-connection basis using SELECT <dbid> where
# dbid is a number between 0 and 'databases'-1
databases 16
10. 是否在启动的时候显示log
always-show-logo yes
11. 持久化规则
redis是内存数据库,如果不进行持久化,则在下次启动的时候会丢失。rdb持久化规则
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
12. 持久化出错是否还继续工作
# However if you have setup your proper monitoring of the Redis server
# and persistence, you may want to disable this feature so that Redis will
# continue to work as usual even if there are problems with disk,
# permissions, and so forth.
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes
13. 是否压缩持久化的rdb的文件,需要消耗一些cpu资源,节约存储空间
# Compress string objects using LZF when dump .rdb databases?
# For default that's set to 'yes' as it's almost always a win.
# If you want to save some CPU in the saving child set it to 'no' but
# the dataset will likely be bigger if you have compressible values or keys.
rdbcompression yes
14. 保存rdb文件的时候,是否校验rdb文件
# RDB files created with checksum disabled have a checksum of zero that will
# tell the loading code to skip the check.
rdbchecksum yes
15. rdb文件名
# The filename where to dump the DB
dbfilename dump.rdb #可以自定义修改
16. rdb文件保存目录
# The working directory.
#
# The DB will be written inside this directory, with the filename specified
# above using the 'dbfilename' configuration directive.
#
# The Append Only File will also be created inside this directory.
#
# Note that you must specify a directory here, not a file name.
dir ./
17. redis主从复制相关配置
################################# REPLICATION #################################
# Master-Slave replication. Use slaveof to make a Redis instance a copy of
# another Redis server. A few things to understand ASAP about Redis replication.
#
# 1) Redis replication is asynchronous, but you can configure a master to
# stop accepting writes if it appears to be not connected with at least
# a given number of slaves.
# 2) Redis slaves are able to perform a partial resynchronization with the
# master if the replication link is lost for a relatively small amount of
# time. You may want to configure the replication backlog size (see the next
# sections of this file) with a sensible value depending on your needs.
# 3) Replication is automatic and does not need user intervention. After a
# network partition slaves automatically try to reconnect to masters
# and resynchronize with them.
#
# slaveof <masterip> <masterport>
# If the master is password protected (using the "requirepass" configuration
# directive below) it is possible to tell the slave to authenticate before
# starting the replication synchronization process, otherwise the master will
# refuse the slave request.
#
# masterauth <master-password>
# When a slave loses its connection with the master, or when the replication
# is still in progress, the slave can act in two different ways:
#
# 1) if slave-serve-stale-data is set to 'yes' (the default) the slave will
# still reply to client requests, possibly with out of date data, or the
# data set may just be empty if this is the first synchronization.
#
# 2) if slave-serve-stale-data is set to 'no' the slave will reply with
# an error "SYNC with master in progress" to all the kind of commands
# but to INFO and SLAVEOF.
#
slave-serve-stale-data yes
# You can configure a slave instance to accept writes or not. Writing against
# a slave instance may be useful to store some ephemeral data (because data
# written on a slave will be easily deleted after resync with the master) but
# may also cause problems if clients are writing to it because of a
# misconfiguration.
#
# Since Redis 2.6 by default slaves are read-only.
#
# Note: read only slaves are not designed to be exposed to untrusted clients
# on the internet. It's just a protection layer against misuse of the instance.
# Still a read only slave exports by default all the administrative commands
# such as CONFIG, DEBUG, and so forth. To a limited extent you can improve
# security of read only slaves using 'rename-command' to shadow all the
# administrative / dangerous commands.
slave-read-only yes
18. redis设置密码
################################## SECURITY ###################################
# Require clients to issue AUTH <PASSWORD> before processing any other
# commands. This might be useful in environments in which you do not trust
# others with access to the host running redis-server.
#
# This should stay commented out for backward compatibility and because most
# people do not need auth (e.g. they run their own servers).
#
# Warning: since Redis is pretty fast an outside user can try up to
# 150k passwords per second against a good box. This means that you should
# use a very strong password otherwise it will be very easy to break.
#
requirepass redis123456 #此处配置持久化密码
19. redis最大内存配置
# NOTE: since Redis uses the system paging file to allocate the heap memory,
# the Working Set memory usage showed by the Windows Task Manager or by other
# tools such as ProcessExplorer will not always be accurate. For example, right
# after a background save of the RDB or the AOF files, the working set value
# may drop significantly. In order to check the correct amount of memory used
# by the redis-server to store the data, use the INFO client command. The INFO
# command shows only the memory used to store the redis data, not the extra
# memory used by the Windows process for its own requirements. Th3 extra amount
# of memory not reported by the INFO command can be calculated subtracting the
# Peak Working Set reported by the Windows Task Manager and the used_memory_peak
# reported by the INFO command.
#
# maxmemory <bytes>
maxmemory 102400000 #此处配置最大内存
20. redis内存达到最大之后的处理策略
# Note: with any of the above policies, Redis will return an error on write
# operations, when there are no suitable keys for eviction.
#
# At the date of writing these commands are: set setnx setex append
# incr decr rpush lpush rpushx lpushx linsert lset rpoplpush sadd
# sinter sinterstore sunion sunionstore sdiff sdiffstore zadd zincrby
# zunionstore zinterstore hset hsetnx hmset hincrby incrby decrby
# getset mset msetnx exec sort
#
# The default is:
#
# maxmemory-policy noeviction
maxmemory-policy 下面的策略
- volatile-7ru: 只对设置了过期时间的key进行LRU(默认值)
- a77keys-7ru : 删除1ru算法的key
- vo1atile-random: 随机删除即将过期key
- a1lkeys-random: 随机删除
- volatile-tt1 : 删除即将过期的
- noeviction : 永不过期,返回错误
21.redis另外一种持久化,aof配置。默认是不开启的
############################## APPEND ONLY MODE ###############################
# AOF and RDB persistence can be enabled at the same time without problems.
# If the AOF is enabled on startup Redis will load the AOF, that is the file
# with the better durability guarantees.
#
# Please check http://redis.io/topics/persistence for more information.
appendonly yes #需要使用aof时,将该参数设置为true
# The name of the append only file (default: "appendonly.aof")
appendfilename "myCache.aof" #aof的文件名
appendonly no 默认不开启
appendfilename "appendonly.aof" aop配置文件名称
appendfsync always ---修改一次,同步一次
appendfsync everysec ----每秒同步一次,可能会丢失一秒的数据
appendfsync no -----不进行同步
22. redis使用命令行设置密码
config set requirepass redis123456 #redis重启后会失效
23. 集群配置
异地多活,主从配置
七 rdb持久化
1.简介
Redis是内存数据库,如果不将内存中的数据库状态保存到磁盘,那么一旦服务器进程退出,服务器中的数据库状态也会消失。所以Redis提供了持久化功能!
RDB流程图:
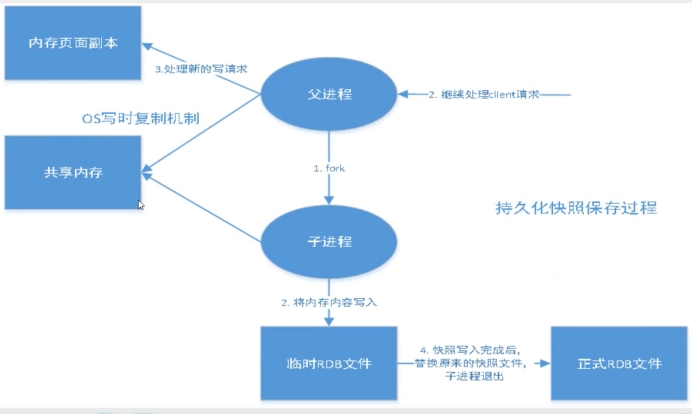
在指定的时间间隔内将内存中的数据集快照写入磁盘,也就是行话讲的Snapshot快照,它恢复时是将快照文件直接读到内存里。
Redis会单独创建 ( fork )一个子进程来进行持久化,会先将数据写入到一个临时文件中,待持久化过程都结束了,再用这个临时文件替换上次持久化好的文件。
整个过程中,主进程是不进行任何IO操作的。这就确保了极高的性能。如果需要进行大规模数据的恢复,且对于数据恢复的完整性不是非常敏感,那RDB方式要比AOF方式更加的高效。RDB的缺点是最后一次持久化后的数据可能丢失。
2.持久化文件产生的方式
达到配置的条件
使用flushdb命令
关闭redis的时候
redis启动的时候,会扫描根目录下的dump.rdb文件,然后进行数据恢复。在生产环境的适合,会对rdb文件进行备份。
优点:
- 适合大规模的数据恢复
缺点:
需要一定的时间间隔,可能会丢失部分时间的数据
需要占用部分的内存空间
八 AOF持久化
1. 以日志的形式来记录每个写操作,将Redis执行过的所有指令记录下来(读操作不记录),只许追加文件但不可以改写文件,redis启动之初会读取该文件重新构建数据,换言之,redis重启的话就根据日志文件的内容将写指令从前到后执行一次以完成数据的恢复工作
2. 默认是不开启的,如果需要使用,需要进行手动配置。
3.如果aof文件有错误,redis在启动的时候没办法启动,此时需要修复aof文件,使用redis-check aof进行恢复,恢复成功后,重启redis即可恢复数据。
4.aof文件达到一定大小后,会新开一个线程重写aof文件
优点:
每次修改都同步,文件完成性更好
每秒修改一次数据就同步,最多丢失一秒的数据
缺点:
占用cpu,运行的效率低于rdb
数据文件大,恢复的时候很慢
九 主从复制
1. 概念
主从复制,是指将一台Redis服务器的数据,复制到其他的Redis服务器。前者称为主节点(master/leader),后者称为从节点
(slave/follower);数据的复制是单向的,只能由主节点到从节点。Master以写为主,Slave以读为主。
默认情况下,每台Redis服务器都是主节点;且一个主节点可以有多个从节点(或没有从节点),但一个从节点只能有一个主节点。
2.作用
主从复制的作用主要包括:
1、数据冗余︰主从复制实现了数据的热备份,是持久化之外的一种数据冗余方式。
2、故障恢复∶当主节点出现问题时,可以由从节点提供服务,实现快速的故障恢复;实际上是一种服务的冗余。
3、负载均衡∶在主从复制的基础上,配合读写分离,可以由主节点提供写服务,由从节点提供读服务(即写Redis数据时应用连接主节点,读Redis数据时应用连接从节点),分担服务器负载;尤其是在写少读多的场景下,通过多个从节点分担读负载,可以大大提高Redis服务器的并发量。
4、高可用基石︰除了上述作用以外,主从复制还是哨兵和集群能够实施的基础,因此说主从复制是Redis高可用的基础
3. 应用
一般来说,要将Redis运用于工程项目中,只使用一台Redis是万万不能的(宕机》,原因如下︰
1、从结构上,单个Redis服务器会发生单点故障,并且一台服务器需要处理所有的请求负载,压力较大;
2、从容量上,单个Redis服务器内存容量有限,就算一台Redis服务器内存容量为256G,也不能将所有内存用作Redis存储内存,一般来说,单台Redis最大使用内存不应该超过20G。
电商网站上的商品,一般都是一次上传,无数次浏览的,说专业点也就是"多读少写"。
十 哨兵模式
1. 概念
主从切换技术的方法是︰当主服务器宕机后,需要手动把一台从服务器切换为主服务器,这就需要人工干预,费事费力,还会造成一段时间内服务不可用。这不是一种推荐的方式,更多时候,我们优先考虑哨兵模式。Redis从2.8开始正式提供了Sentinel(哨兵)架构来解决这个问题。
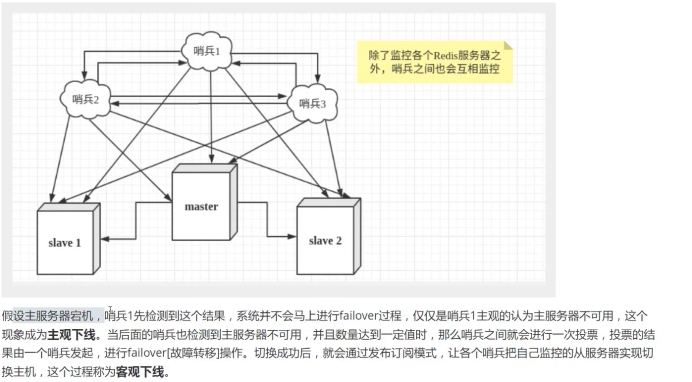
谋朝篡位的自动版,能够后台监控主机是否故障,如果故障了根据投票数自动将从库转换为主库。
哨兵模式是一种特殊的模式,首先Redis提供了哨兵的命令,哨兵是一个独立的进程Ⅰ作为进程,它会独立运行。其原理是哨兵通过发送命令,等待Redis服务器响应,从而监控运行的多个Redis实例。
2. 作用
- 通过发送命令,让Redis服务器返回监控其运行状态,包括主服务器和从服务器。
- 当哨兵监测到master宕机,会自动将slave切换成master,然后通过发布订阅模式通知其他的从服务器,修改配置文件,让它们切换主机。
然而一个哨兵进程对Redis服务器进行监控,可能会出现问题,为此,我们可以使用多个哨兵进行监控。各个哨兵之间还会进行监控,这样就形成了多哨兵模式。
3. 配置
- 新建一个sentinel.conf的配置文件,配置监控哪一个主节点
- sentinel monitor myredis 127.0.0.1 6379 1 myredis-哨兵名称 127.0.0.1 6379--监控的节点 1--后面的这个数字1,代表主机挂了,slave投票看让谁接替成为主机,票数最多的,就会成为主机 !
优点:
- 哨兵集群,基于主从复制,所有主从复制的优点,他全有
- 主从可以切换,故障可以转移,系统的可用性会很好
缺点:
- 不好在线扩容,如果redis集群容量已经满了,在线扩容十分麻烦
- 配置复杂
十一 缓存穿透
描述:当用户请求到达redis缓存时,如果此时缓存中不存在该查询对象时,会转到mysql数据库中查询,如果此时mysql数据中也没有,该请求就会循环从缓存到数据库。当受到恶意攻击或者并发量大的时候,严重的情况下会使数据库宕机。
解决方案1
布隆过滤器:
布隆过滤器是一种数据结构,对所有的查询参数进行hash存储,在控制层先进行校验,如果不符合则直接丢弃,从而减小了底层存储库的压力
解决方案2
对空值进行缓存:
当查询条件从redis没有查询到数据,也在mysql中查询不到数据,此时直接针对该条件进行空值缓存,这样就避免了在高并发的情况下,对mysql数据库造成过大压力
问题:
- 如果空值能够被缓存起来,这就意味着缓存需要更多的空间存储更多的键,因为这当中可能会有很多的空值的键;
- 即使对空值设置了过期时间,还是会存在缓存层和存储层的数据会有一段时间窗口的不一致,这对于需要保持一致性的业务会有影响。
十二 缓存击穿(查询太多)
描述:非常热点的key,集中打到同一个点。比如微博热搜,对一个热点数据进行缓存,设置60秒的过期时间,然后再60.1秒的时候恢复,但是0.1秒内的请求非常的大,也会集中打到数据库。
解决方案:
1. 热点数据不设置过期时间,或根据业务设置更长的过期时间
2. 分布式锁,当缓存击穿的时候,设置在同一时间访问数据库的线程只有一个。这样也能避免数据库受到高并发的请求。
十三 缓存雪崩
描述:热点的key在集中的时间内集体失效,导致请求直接打到数据库,导致数据库崩溃
解决方案:
1. 增加mysql集群,异地多活
2. 数据 限流,降级
3. 数据预热:数据加热的含义就是在正式部署之前,我先把可能的数据先预先访问一遍,这样部分可能大量访问的数据就会加载到缓存中。在即将发生大并发访问前手动触发加载缓存不同的key,设置不同的过期时间,让缓存失效的时间点尽量均匀。
- 本文标签: redis
- 本文链接: https://www.tianyajuanke.top/article/28
- 版权声明: 本文由吴沛芙原创发布,转载请遵循《署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)》许可协议授权













