springboot核心技术与响应式编程二
一. 配置文件
1. yml的用法
yml中配置实体类对应的属性
user:
userName: zhangsan
age: 18
birthday: 2020/01/05
animal: ['小猫',小狗,小猪] #数组写法
intrests: #数组写法
- 美女
- 电影
- 运动
socre: #对象写法
english: 88
yuwen: 90
salarys:
- 88.55
- 88.66
- 88.77
pet:
petName: 小花
petAge: 2
allPets:
love:
- petName: 小花
petAge: 2
- petName: 小哈
petAge: 1
hate:
- petName: 小泰迪
petAge: 1
nomarl: [{petName: 小猪,petAge: 3 }]
实体类
@ToString
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
@Data
public class SysUser {
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
private List<String> animal;
private String[] intrests;
private Map<String,Object> socre;
private Set<Double> salarys;
private Map<String,List<Pet>> allPets;
private Pet pet;
}
@Data
public class Pet {
private String petName;
private Integer petAge;
}
2. 自定义绑定配置提示
二. web开发
1. web开发简介
2. 静态资源规则与定制化
(1). 静态资源目录
静态资源路径META-INFO/resources public resources static
访问:当前项目根路径+静态资源名
原理:静态映射/**
请求发到处理器,先在controller查找有没有对应的映射,如果没有,则再去静态资源寻找
(2)静态资源访问目录
自定义静态资源访问路径。
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /test/**
访问: 当前根路径+static-path-pattern设置的路径+资源名称
修改静态资源目录。根路径下的test为静态资源目录
spring:
web:
resources:
static-locations: classpath:/test/
(3)流行的web目录
webjar自动映射
引入jequery
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.6.0</version>
</dependency>
访问:当前根路径/webjar/jequery/xxxx
原理,在WebMvcAutoConfiguration配置类中,资源处理的默认规则配置webjar的映射规则。
如果spring.web.resources.add-mappings设置为false 将会禁用所有静态资源规则
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//如果spring.web.resources.add-mappings设置为false 将会禁用所有静态资源规则
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> {
registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
if (this.servletContext != null) {
ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION);
registration.addResourceLocations(resource);
}
});
}
3. welcome和favicion功能
静态资源路径下 index.html
可以配置静态资源
不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀,否则不能访问到index.html
可以处理/index
favicon.ico 放在静态资源目录下
spring:
# mvc:
# static-path-pattern: /res/** 这个会导致 Favicon 功能失效
4. 源码分析-静态资源原理
- springboot启动默认加载xxxAutoConfiguration类(自动配置类)
- SpringMVC功能的自动配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration生效
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
- 在容器中配置的mvc自动配置适配器
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ResourceProperties.class, WebProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware {
关键内容WebMvcProperties.class ResourceProperties.class WebProperties.class
WebMvcProperties对应spring.mvc
ResourceProperties对应spring.resources
WebProperties对应spring.web
ResourceProperties默认路径
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
三 请求参数处理
1.rest映射及源码分析
对于get post delete put四个请求,表单提交能正常提交get和post,但是delete和put需要进行相关配置处理
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Get请求";
}
@PostMapping("/hello")
public String helloPost() {
return "Post请求";
}
@DeleteMapping("/hello")
public String helloDelete() {
return "Delete请求";
}
@PutMapping("/hello")
public String helloPut() {
return "Putt请求";
}
springmvc自动配置类介绍(请求头过滤器)
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = "enabled") public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() { return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter(); }容器中没有配置HiddenHttpMethodFilter类才会自动加载该配置
spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter.enabled为true才会开启该配置(默认为false)
/** * Specify if the condition should match if the property is not set. Defaults to * {@code false}. * @return if should match if the property is missing */ boolean matchIfMissing() default false;表单提交方式需要为post,带上配置中的参数_method,并指定请求方式
@Override protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request; //请求方式为post 并且请求头无错误 if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) == null) { //获取参数值this.methodParam默认为_method String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam); //如果_mothod有值 if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) { //进行大写转换 String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH); //如果该请求方式在允许的请求类型中,则进行RequestWrapper转换放行 //ALLOWED_METHODS 包含PUT DELETE PATCH if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) { requestToUse = new HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method); } } } filterChain.doFilter(requestToUse, response); }
表单请求方式
<form method="get" action="/hello"> <input name="get" value="get-请求" type="submit"> </form> <form method="post" action="/hello"> <input name="post" value="post-请求" type="submit"> </form> <form method="post" action="/hello"> <input name="_method" value="delete" hidden="true"> <input name="delete" value="delete-请求" type="submit"> </form> <form method="post" action="/hello"> <input name="_method" value="put" hidden="true"> <input name="put" value="put-请求" type="submit"> </form>仅针对表单提交的请求方式进行修改,其他rest请求工具 如postMan,则不会进行该处理
2. 修改默认的_method
通过源码分析,真正起作用的是HiddenHttpMethodFilter类,该类中有设置methodParam的方法
public void setMethodParam(String methodParam) { Assert.hasText(methodParam, "'methodParam' must not be empty"); this.methodParam = methodParam; }由上分析,可以在配置类中配置,然后进行请求头参数方法设置
@Bean public HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter(){ HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter(); hiddenHttpMethodFilter.setMethodParam("_hello"); return hiddenHttpMethodFilter; }
3. 请求映射原理
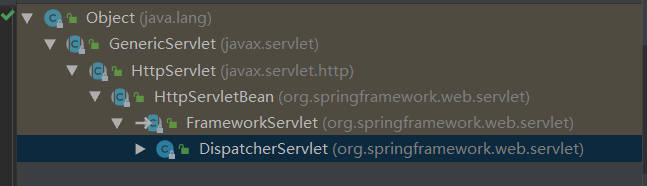
FrameworkServlet重写了HttpServlet的do Get/Post/delete/post等方法,都转到processRequest()方法
processRequest()方法最终进行doService方法处理,但是doService方法是一个抽象方法,且当前类没有实现,所以只能调用子类DispatcherServlet的doService方法
//Subclasses must implement this method to do the work of request handling, 子类必须实现该方法进行请求处理 protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;DispatcherServlet的doService方法,最终进行请求映射的是doDispatch(request, response);
doDispatch-》checkMultipart(将请求转换为多部分请求,并使多部分解析器可用,如果没有设置多部分解析器,只需使用现有请求即可)
最后是getHandler(为当前请求匹配处理器)
// Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { //this.handlerMappings = List<HandlerMapping> 从容器中获取的请求处理器 if (this.handlerMappings != null) { //遍历获取到的所有处理器 for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { //将请求处理器和当前请求进行匹配,如果匹配到了,则返回对应的处理器 HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null; }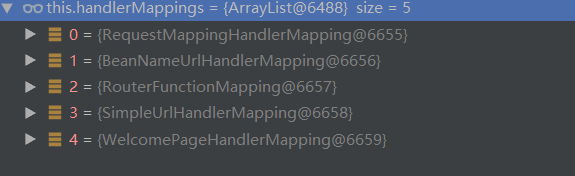
总结流程:前端请求到达前端控制器DispatcherServlet(doService) ---> 转到请求适配doDispatch()----> 转到请求映射处理器getHandler()--》返回匹配到的请求处理器-------》视图解析,返回前端等
4. 常用参数注解
常用参数注解都可以使用Map
@PathVariable 路径变量,用于获取rest请求路径上的参数
@RequestHeader 获取请求头,请求头中携带的参数
@RequestParam 获取请求参数,url请求中?号后的请求参数获取
@CookieValue 获取cookie值,获取cookie中的数据
@RequestBody 获取请求体数据(post)
@RequestAttribute 获取request域属性
//在test请求中存放的id和code参数,转发到success @GetMapping("/test") public String test(HttpServletRequest request) { request.setAttribute("id","9527"); request.setAttribute("code",200); return "forward:/success"; } //在success页面可以通过原生的request进行attribute参数获取,也可通过@RequestAttribute注解进行获取 @ResponseBody @GetMapping("/success") public Map success(HttpServletRequest request,@RequestAttribute("id") String attId) { Object id = request.getAttribute("id"); HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("id1",id); map.put("id2",attId); return map; }@MatrixVariable 矩整变量
- 在springboot中,mvc自动配置的urlPathhelper将移除url分号内容默认设置为true,所以需要使用矩整变量功能,需要先开启
//UrlPathHelper中 private boolean removeSemicolonContent = true;开启矩整变量功能
1. 在配置文件中配置WebMvcConfigurer,并重写configurePathMatch方法,在该方法中配置UrlPathHelper,设置移除url分号内容为false @Bean public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){ return new WebMvcConfigurer(){ @Override public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) { UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper(); urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false); configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper); } }; } 2. 配置类实现WebMvcConfigurer,然后重写configurePathMatch方法,在该方法中配置UrlPathHelper,设置移除url分号内容为false import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.PathMatchConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper; @Configuration public class MyMvcConfigurer implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) { UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper(); urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false); configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper); } }矩整变量参数携带方式
1.url参数,都为一一对应 /matrix/9527;age=10;sex=1;name=王,李,赵 // url= /matrix/9527,参数==》》age=10;sex=1;name=王,李,赵 //后台接收解析 @ResponseBody @GetMapping("/matrix/{path}") public Map matrix(@MatrixVariable("age") Integer age, @MatrixVariable("sex")Integer sex, @MatrixVariable("name")List<String> name ,@PathVariable("path")String path) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("age",age); map.put("sex",sex); map.put("name",name); map.put("path",path); return map; } 2. url参数为a对应a,b对应b /matrix/9527;age=10/9528;age=20 //url /matrix/{id}/{id2} 参数===》》id参数为age=10 id2参数为 age=20 //后台解析 @MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "userId") value代表获取哪个值,pathVar获取哪个参数 @ResponseBody @GetMapping("/matrix/{userId}/{eqId}") public Map matrix( @MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "userId") Integer userId, @MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "eqId") Integer eqId ) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("age1", userId); map.put("age2", eqId); return map; }
5. 请求参数处理原理
- handlerMapping中找到能处理请求的Handler(Controller.method())
- 为当前handler找到一个适配器
适配器执行目标方法确定方法参数的每一个值
找到handlerAdpter
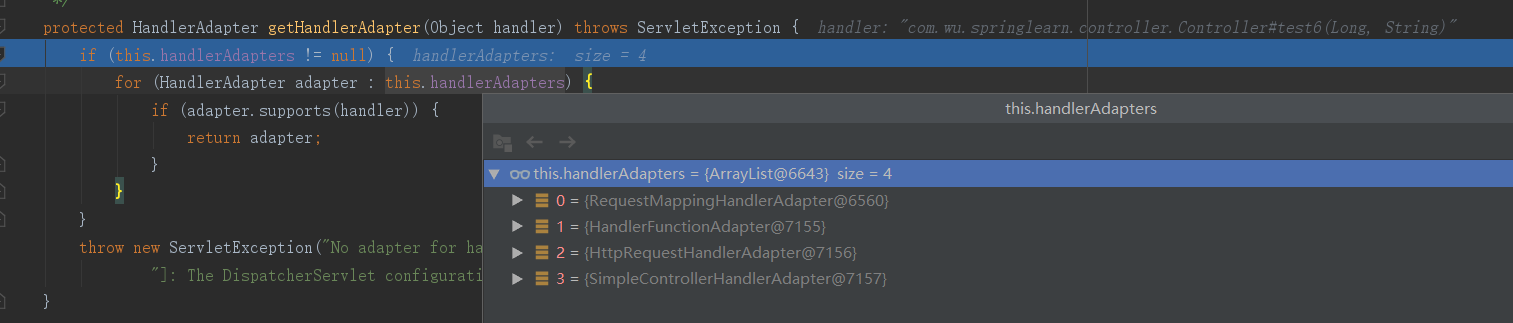
支持方法上标注RequestMapping
支持函数式编程
执行目标方法
// Actually invoke the handler.
1. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
//处理请求参数
2. mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
3.invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
4. Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
//获取方法的参数值
5. Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
======RequestMappingHandlerAdapter=========
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
//重新生成一个webRequest
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
//生成一个可用的处理方法的handler
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
//设置参数解析器 this.argumentResolvers中有27种解析器
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
//调用处理器
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
参数解析器HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
springMVC目标方法能写多少种参数类型,取决于参数解析器
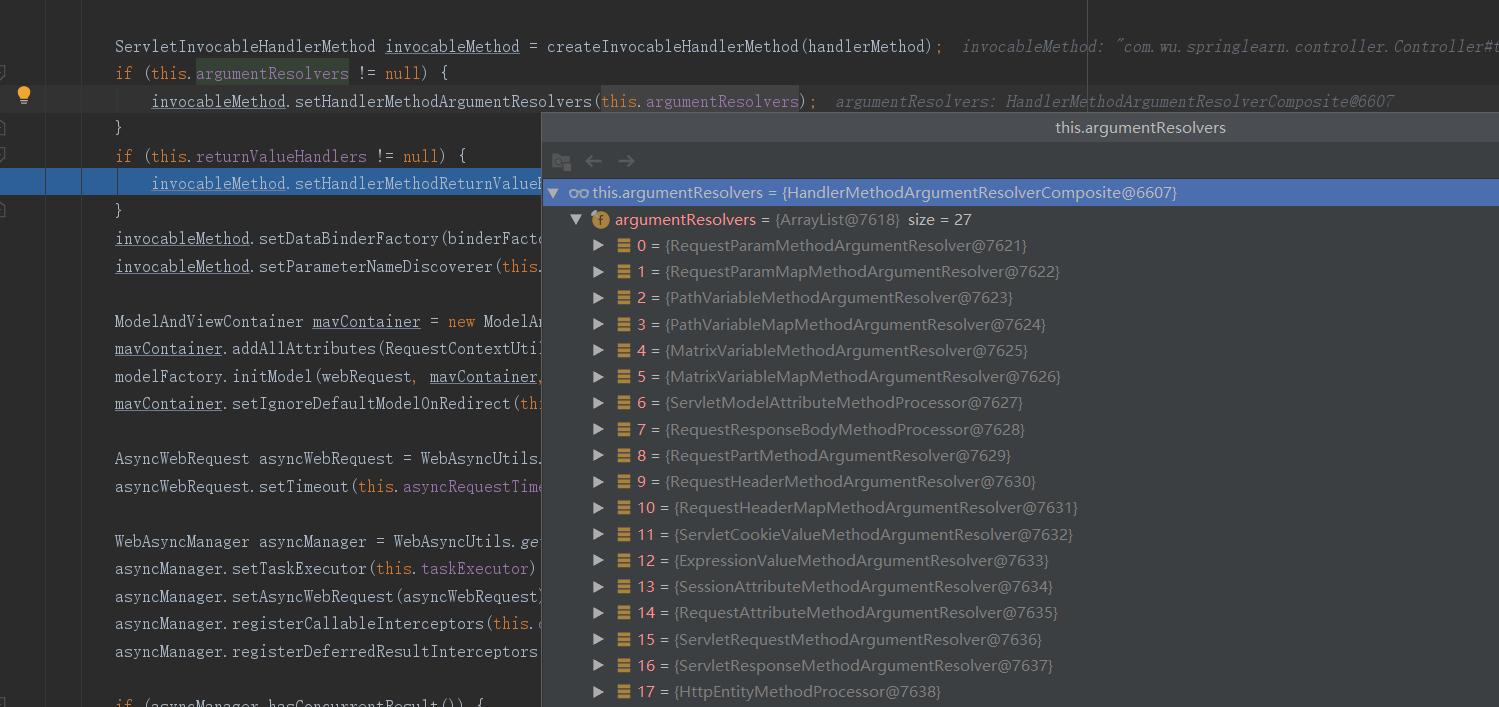
参数解析器确定目标方法的参数值
====InvocableHandlerMethod==== protected Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters(); if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameters)) { return EMPTY_ARGS; } Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length]; for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) { MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i]; parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer); args[i] = findProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs); if (args[i] != null) { continue; } if (!this.resolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) { throw new IllegalStateException(formatArgumentError(parameter, "No suitable resolver")); } try { args[i] = this.resolvers.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory); } catch (Exception ex) { // Leave stack trace for later, exception may actually be resolved and handled... if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String exMsg = ex.getMessage(); if (exMsg != null && !exMsg.contains(parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString())) { logger.debug(formatArgumentError(parameter, exMsg)); } } throw ex; } } return args; }返回值处理器
===ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle==== this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue( returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
6. 自定义参数映射原理
//接口
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/getMyUser")
public MyUser getMyUser( MyUser myUser) {
return myUser;
}
//用户对象
public class MyUser {
private String userName;
private Integer userAge;
private Pet pet;
}
//宠物对象
public class Pet {
private String petName;
private Integer petAge;
}
//请求表单
<form method="post" action="/getMyUser">
<input name="userName" value="张三 ">
<input name="userAge" value="20">
<input name="pet.petName" value="hello kity">
<input name="pet.petAge" value="2">
<input value="提交" type="submit">
</form>
请求参数解析总结:
//ps:断点打在doDispatch方法内,每个步骤对应1个或多个方法进入
//DispatcherServlet.doDispatch方法种执行处理方法
1. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
//RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.handleInternal方法中执行处理方法
2.mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
//RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.invokeHandlerMethod方法中经过一系列初始化方法后,执行处理handler
//其中包含设置参数解析器invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
//设置返回值解析器 invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
3. invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
//ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle中执行request处理方法,并返回值
4.Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
//InvocableHandlerMethod.invokeForRequest 继续执行
5.Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
6.getMethodArgumentValues方法中进行参数处理
6.1 判断是否支持提交的参数 !this.resolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)
//从27种参数解析器中匹配是否有支持该参数的方法,匹配到后返回
private HandlerMethodArgumentResolver getArgumentResolver(MethodParameter parameter) {
//先从缓存获取
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver result = this.argumentResolverCache.get(parameter);
if (result == null) {
//再从容器中获取进行比对判断
for (HandlerMethodArgumentResolver resolver : this.argumentResolvers) {
if (resolver.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
result = resolver;
//匹配成功,放入缓存
this.argumentResolverCache.put(parameter, result);
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
6.2 解析参数 args[i] = this.resolvers.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);
ModelAttributeMethodProcessor.resolveArgument方法中进行参数绑定
public final Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
Assert.state(mavContainer != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires ModelAndViewContainer");
Assert.state(binderFactory != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires WebDataBinderFactory");
//获取参数类名称
String name = ModelFactory.getNameForParameter(parameter);
ModelAttribute ann = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
if (ann != null) {
mavContainer.setBinding(name, ann.binding());
}
Object attribute = null;
BindingResult bindingResult = null;
if (mavContainer.containsAttribute(name)) {
attribute = mavContainer.getModel().get(name);
}
else {
// Create attribute instance
try {
//创建参数对象空实例
attribute = createAttribute(name, parameter, binderFactory, webRequest);
}
catch (BindException ex) {
if (isBindExceptionRequired(parameter)) {
// No BindingResult parameter -> fail with BindException
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, expose null/empty value and associated BindingResult
if (parameter.getParameterType() == Optional.class) {
attribute = Optional.empty();
}
else {
attribute = ex.getTarget();
}
bindingResult = ex.getBindingResult();
}
}
if (bindingResult == null) {
// Bean property binding and validation;
// skipped in case of binding failure on construction.
//创建绑定关系
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name);
if (binder.getTarget() != null) {
if (!mavContainer.isBindingDisabled(name)) {
//进行参数绑定
bindRequestParameters(binder, webRequest);
}
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new BindException(binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
// Value type adaptation, also covering java.util.Optional
if (!parameter.getParameterType().isInstance(attribute)) {
attribute = binder.convertIfNecessary(binder.getTarget(), parameter.getParameterType(), parameter);
}
bindingResult = binder.getBindingResult();
}
// Add resolved attribute and BindingResult at the end of the model
Map<String, Object> bindingResultModel = bindingResult.getModel();
mavContainer.removeAttributes(bindingResultModel);
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(bindingResultModel);
return attribute;
}
6.3参数绑定中的参数处理AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor.processLocalProperty (由bindRequestParameters方法进入,进行多层级方法到参数处 理方法)
由转换器进行参数值处理,将原参数处理成对象类型的参数
valueToApply = convertForProperty(
tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, originalValue, ph.toTypeDescriptor());
- 本文标签: Java Spring Boot Spring
- 本文链接: https://www.tianyajuanke.top/article/37
- 版权声明: 本文由吴沛芙原创发布,转载请遵循《署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)》许可协议授权












