Mybatis-Plus自定义全局方法
一 前言
最近做的一个项目是地理信息相关的,包含了一些地理位置信息字段,如Point ,Line,Geometry,数据库采用的是PostGreSql+Postgis ,数据库框架使用Mybatis-Plus。。。。
mybatis-plus帮我们封装了大部分的CURD脚本,在进行日常增删改查分页等都能节约大量的时间,但是在遇到特殊字段的时候,如即将要插入的数据中包含一个point字段,此时使用mybatis-plus自带的mapper.insert() 或service.save()方法就不行了,此时就只能去xml中写sql。如需要插入一个用户数据,用户id和用户名不为空,但是用户的手机号和用户的位置信息可能为空,因为用户的位置字段是点,在插入数据库的时候需要进行处理,mybatis-Plus在插入数据的时候没有处理方法,所以需要在xml中手写sql。如下
<!--该sql纯手写,未经验证,仅用于描述-->
insert into sys_user(id,name,phone,point)
values (
#{user.id},
#{user.name},
<choose>
<when test="null!=user.phone and ''!=user.phone">
#{user.phone},
</when>
<otherwise>
'18888888888',
</otherwise>
</choose>
<choose>
<when test="null!=user.point and ''!=user.point">
ST_GeomFromText(concat('POINT(',#{user.point},')'), 4490)
</when>
<otherwise>
null
</otherwise>
</choose>
)
当很多地方都需要处理字段的时候,插入数据将会写非常多的sql,就没有达到使用框架简化代码量的效果。
二 源码分析
官网地址https://baomidou.com/pages/42ea4a/
官网中简要介绍了SQL注入器配置:全局配置 sqlInjector 用于注入 ISqlInjector 接口的子类,实现自定义方法注入。 为达到知其然并知其所以然的目的,进行了一次简单的源码分析。
我使用的是3.3.0版本,源码结构在某些地方会和大家的有些差异,分析的时候只着重关注重要的源码块。
1.框架结构
来源官网
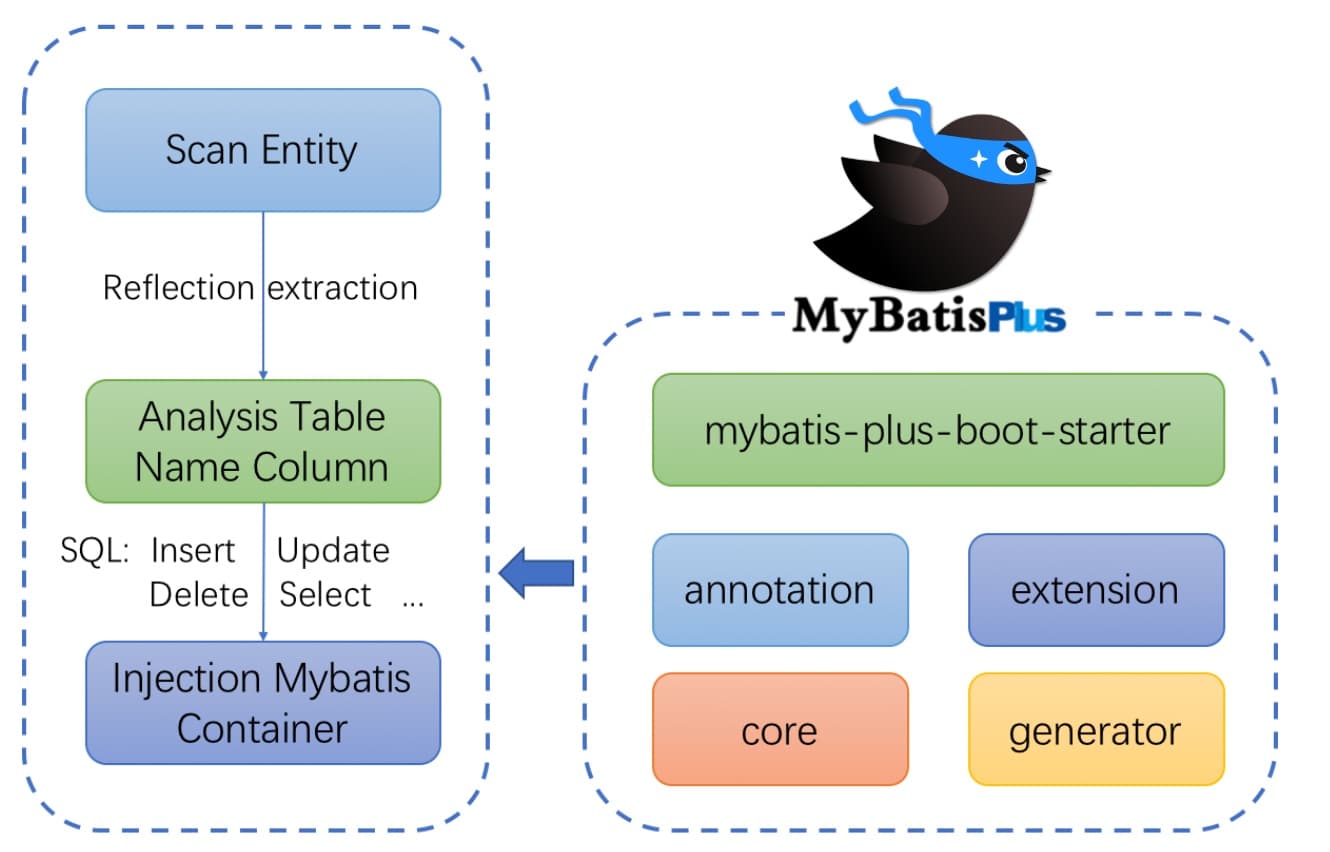
2. mybatis-plus-boot-starter
xxx-boot-starter都是xxx框架的自动配置块,他们的自动配置类一般都是xxxAutoConfiguration。
1. 查看关键配置
在MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration自动配置中找到了sql注入器的配置方法,查看ISqlInjector在该版本下如何注入的。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
//前面省略了部分代码
......
// TODO 自定义枚举包
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeEnumsPackage())) {
factory.setTypeEnumsPackage(this.properties.getTypeEnumsPackage());
}
// TODO 此处必为非 NULL
GlobalConfig globalConfig = this.properties.getGlobalConfig();
// TODO 注入填充器
this.getBeanThen(MetaObjectHandler.class, globalConfig::setMetaObjectHandler);
// TODO 注入主键生成器
this.getBeanThen(IKeyGenerator.class, i -> globalConfig.getDbConfig().setKeyGenerator(i));
// TODO 注入sql注入器
this.getBeanThen(ISqlInjector.class, globalConfig::setSqlInjector);
// TODO 注入ID生成器
this.getBeanThen(IdentifierGenerator.class, globalConfig::setIdentifierGenerator);
// TODO 设置 GlobalConfig 到 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean
factory.setGlobalConfig(globalConfig);
return factory.getObject();
}
2. 查看全局配置
public class GlobalConfig implements Serializable {
.....省略上下部分代码,节约空间
/**
* 数据库相关配置
*/
private DbConfig dbConfig;
/**
* SQL注入器,此处使用默认的SQL注入器
*/
private ISqlInjector sqlInjector = new DefaultSqlInjector();
/**
* Mapper父类
*/
private Class<?> superMapperClass = Mapper.class;
.......
}
3.core
Mybatis-Plus的核心包,所有的功能都在该模块能找到。其中injector(注入器)包下的结构如下:
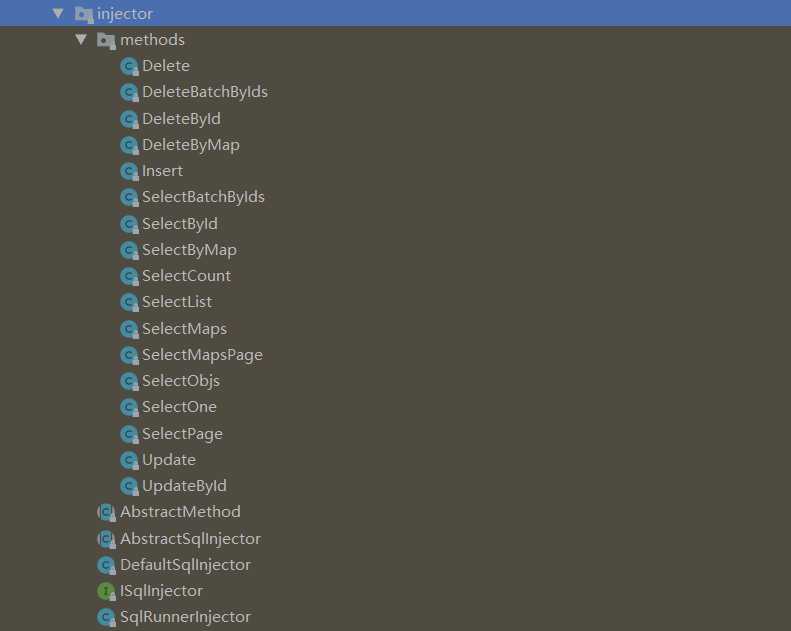
看到这些crud的方法,就明白了为什么MybatisPlus能让让我们不用再手写sql了,因为都在这些方法中把sql脚本写好了。以下是Insert源码
public class Insert extends AbstractMethod {
@Override
public MappedStatement injectMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo) {
//主键生成策略,@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = new NoKeyGenerator();
//插入一条数据,选择有值的数据插入,详情见SqlMethod
SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.INSERT_ONE;
//类modelClass对应列的处理脚本
String columnScript = SqlScriptUtils.convertTrim(tableInfo.getAllInsertSqlColumnMaybeIf(),
LEFT_BRACKET, RIGHT_BRACKET, null, COMMA);
//类modelClass对应值的处理脚本
String valuesScript = SqlScriptUtils.convertTrim(tableInfo.getAllInsertSqlPropertyMaybeIf(null),
LEFT_BRACKET, RIGHT_BRACKET, null, COMMA);
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
// 表包含主键处理逻辑,如果不包含主键当普通字段处理
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(tableInfo.getKeyProperty())) {
if (tableInfo.getIdType() == IdType.AUTO) {
/** 自增主键 */
keyGenerator = new Jdbc3KeyGenerator();
keyProperty = tableInfo.getKeyProperty();
keyColumn = tableInfo.getKeyColumn();
} else {
if (null != tableInfo.getKeySequence()) {
keyGenerator = TableInfoHelper.genKeyGenerator(getMethod(sqlMethod), tableInfo, builderAssistant);
keyProperty = tableInfo.getKeyProperty();
keyColumn = tableInfo.getKeyColumn();
}
}
}
//格式化sql 不懂的可以去百度 java format方法
String sql = String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), tableInfo.getTableName(), columnScript, valuesScript);
//创建sql源
SqlSource sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, sql, modelClass);
return this.addInsertMappedStatement(mapperClass, modelClass, getMethod(sqlMethod), sqlSource, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn);
}
}
4. SQL注入器配置
定义各类CURD脚本方法,继承AbstractMethod(抽象注入方法类)
在自定义的脚本方法中根据需求编写脚本
自定义SQL注入器,实现ISqlInjector(sql注入器)接口,将自定义的脚本方法加入自定义的SQL注入器中,参考DefaultSqlInjector(默认sql注入器)
编写自定义的Mapper,继承Mapper类
如果仅是在原mapper基础上扩展,则自定义的SQL注入器继承DefaultSqlInjector的sql注入器,自定义的mapper继承BaseMapper即可
实体类对应的Mapper继承我们自定义的Mapper
修改全局配置的默认SQL注入器为自定义的SQL注入器
顺序不分先后,但都是必要流程。
三 自定义全局配置
1. 自定义Insert方法
insert方法
//自定义插入逻辑,在原insert方法基础上进行修改
public class InsertGeometry extends AbstractMethod {
@Override
public MappedStatement injectMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo) {
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = new NoKeyGenerator();
SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.INSERT_ONE;
String columnScript = SqlScriptUtils.convertTrim(tableInfo.getAllInsertSqlColumnMaybeIf(),
LEFT_BRACKET, RIGHT_BRACKET, null, COMMA);
String valuesScript = SqlScriptUtils.convertTrim(tableInfo.getAllInsertSqlPropertyMaybeIf(null),
LEFT_BRACKET, RIGHT_BRACKET, null, COMMA);
//修改start
//此处将生成的脚本,通过自定义的字段注解方法替换成预期脚本
Field[] fields = modelClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
//判断该字段是否加了MyTableField(自定义)注解
MyTableField annotation = field.getAnnotation(MyTableField.class);
if (null != annotation) {
valuesScript = MyBatisHandleUtil.replaceGeomColumn(field.getName(),annotation.geomType(),valuesScript);
}
}
//修改end
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
// 表包含主键处理逻辑,如果不包含主键当普通字段处理
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(tableInfo.getKeyProperty())) {
if (tableInfo.getIdType() == IdType.AUTO) {
/** 自增主键 */
keyGenerator = new Jdbc3KeyGenerator();
keyProperty = tableInfo.getKeyProperty();
keyColumn = tableInfo.getKeyColumn();
} else {
if (null != tableInfo.getKeySequence()) {
keyGenerator = TableInfoHelper.genKeyGenerator(getMethod(sqlMethod), tableInfo, builderAssistant);
keyProperty = tableInfo.getKeyProperty();
keyColumn = tableInfo.getKeyColumn();
}
}
}
String sql = String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), tableInfo.getTableName(), columnScript, valuesScript);
SqlSource sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, sql, modelClass);
//注意,此处的insertGeometry一定要和自定义mapper中的方法名一致
return this.addInsertMappedStatement(mapperClass, modelClass, "insertGeometry", sqlSource, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn);
}
}
MyTableField注解
/**
* remark: 自定义空间字段注解
*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface MyTableField {
//空间字段类型,默认为其他类型
GeometryField geomType() default GeometryField.DEFAULT;
}
MyBatisHandleUtil类
public class MyBatisHandleUtil {
//统一处理方法,思路一致,可根据需求做不同处理
public static String replaceGeomColumn(String fieldName, GeometryField geometryField, String valuesScript) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("#{");
sb.append(fieldName);
sb.append("}");
//至于为什么这样写替换目标值,参考原valuesScript处理后的返回值
if (geometryField.equals(GeometryField.POINT)) {
//注解为点的处理
return valuesScript.replace(sb.toString(), "ST_GeomFromText(concat('POINT('," + sb.toString() + ",')'), 4490)");
} else if (geometryField.equals(GeometryField.LINE)) {
//注解为线的处理
return valuesScript.replace(sb.toString(), "ST_GeomFromText(concat('LINESTRING('," + sb.toString() + ",')'), 4490)");
} else if (geometryField.equals(GeometryField.GEOM)) {
//注解为面的处理
return valuesScript.replace(sb.toString(), "ST_GeomFromText(concat('POLYGON('," + sb.toString() + ",')'), 4490)");
}
return valuesScript;
}
}
GeometryField枚举类
//空间类型枚举类
public enum GeometryField {
/**
* remark:默认就是其他类型,不做处理
*/
DEFAULT,
/**
* remark:点
*/
POINT,
/**
* remark:线
*/
LINE,
/**
* remark:面
*/
GEOM
}
2. 自定义sql注入器
//自定义全局sql处理,在原mapper上新增
public class MyLogicSqlInjector extends DefaultSqlInjector {
@Override
public List<AbstractMethod> getMethodList(Class<?> mapperClass) {
//此处调用默认sql注入器的方法,放到自定义的方法中
List<AbstractMethod> methodList = super.getMethodList(mapperClass);
//自定义的插入方法
methodList.add(new InsertGeometry());
return methodList;
}
}
3. 自定义的mapper
@Mapper
public interface MyBaseMapper<T> extends BaseMapper<T> {
//注意,此处的方法名insertGeometry一定要和自定义脚本方法中的方法名一致
int insertGeometry(T entity);
}
4. 配置自定义的SQL注入器
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
//自定义的SQL注入器配置到IOC中
@Bean
public MyLogicSqlInjector myLogicSqlInjector() {
return new MyLogicSqlInjector();
}
//待容器中生成GlobalConfig配置后,再配置自定义的sql注入器
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(GlobalConfig.class)
public GlobalConfig globalConfig(GlobalConfig config){
return config.setSqlInjector(myLogicSqlInjector());
}
}
5. 实体类对应的Mapper继承自定义mapper
@Mapper
public interface SysUserDao extends MyBaseMapper<SysUserEntity> {
}
6.实体类
@Data
public class UserEntity {
private Long userId;
private String userName;
private String userPhone;
//数据库中是点类型的字段,后续有线或面的字段,可以通过GeometryField进行调整
@MyTableField(geomType = GeometryField.POINT)
private String point;
}
7. 测试
@Test
public void test(){
UserEntity entity = new UserEntity();
entity.setId(YitIdHelper.nextId());
entity.setName("王小虎");
entity.setPoint("116.446238 39.937289");
sysUserDao.insertGeometry(entity);
}
Preparing sql输出为
insert into sys_user (id,name,phone,point) values (?,?,?,ST_GeomFromText(concat('POINT(',?,')'), 4490))
- 本文标签: Java mybatisPlus
- 本文链接: https://www.tianyajuanke.top/article/66
- 版权声明: 本文由吴沛芙原创发布,转载请遵循《署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)》许可协议授权













